Stabbing knee pain that comes and goes
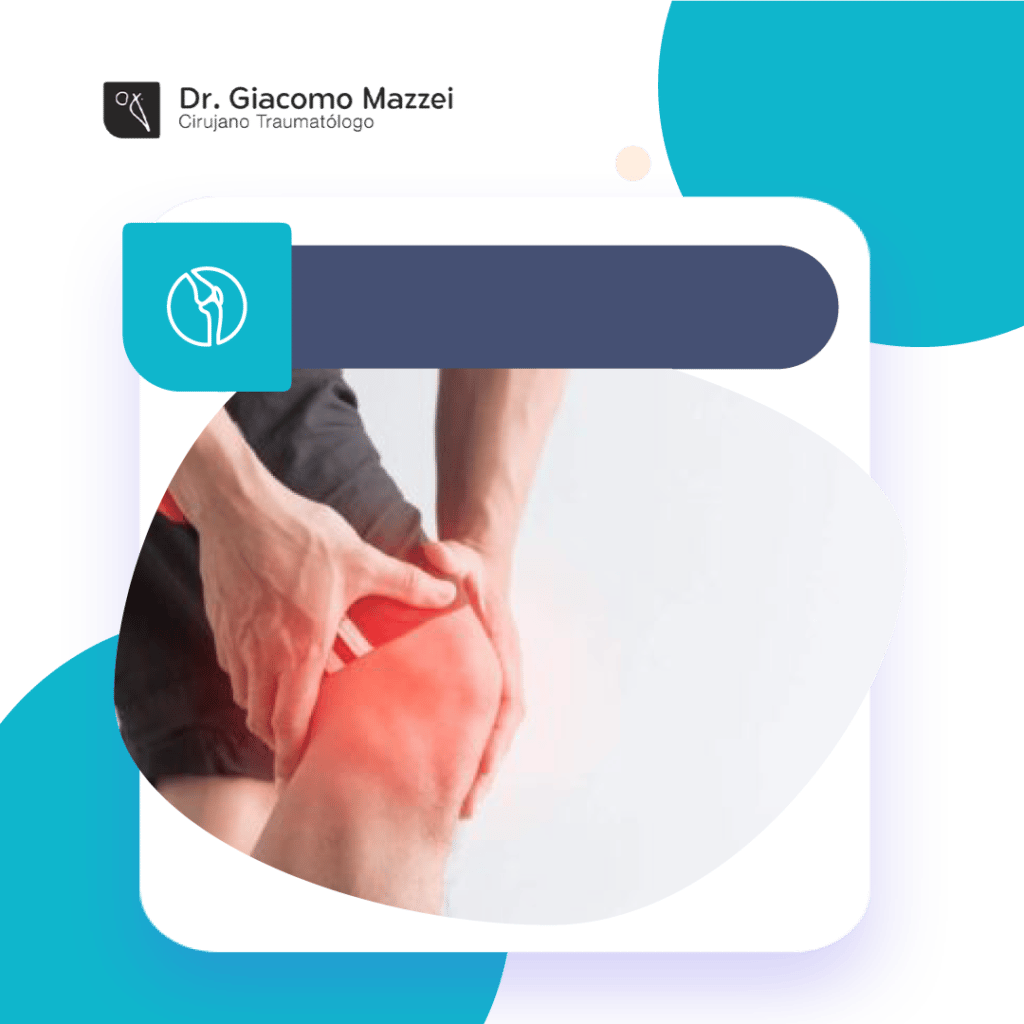
Stabbing pain in the knee can be exceptionally unpleasant, and often leaves people in the lurch. It usually suggests a problem in one of the bones of the knee or in the soft tissues.
Acute knee pain is usually short-lived, starting suddenly with a particular activity and then quickly relieving when the offending activity stops.
- Rupture of the knee cartilage: Joint damage that, if not fixed, can evolve into a degenerative process of the entire knee.
- Knee bursitis: Inflammation of the pre-patellar bursa.
- Septic arthritis: Intra-articular knee infection that requires immediate intervention.
- Dislodged body: Foreign body mobilized within the joint.
- Bone fracture: Bone fracture that may require surgery.
- Nerve irritation: Condition of compression or fibrosis that traps the nerve.
- Exercise routinely. Although exercise can contribute to some leg pain, exercise sessions at least twice a week helped reduce pain when walking as well as increase the distance a person can walk.
- Stop smoking cigarettes. Cigarette smoking is a major risk factor for acute pain when walking. Smoking cigarettes can cause changes in blood vessels, as well as facilitate blood embolisms, which can increase leg pain.
- Follow a heart-healthy diet. Choosing a heart-healthy diet plan can help you maintain your weight as well as blood glucose levels. This can help reduce several of the risk aspects that can cause stabbing knee pain.
- Cross training. If your leg pain is related to overuse of physical activity, try a new activity that is less repetitive for your legs and feet.
- Consult your doctor. If none of the above works, you should opt for a visit to your trusted traumatologist for a professional evaluation.
- Maintaining a healthy, balanced weight and taking care of your body can help reduce sharp, stabbing pain whenever possible.
Do you need an appointment with a professional doctor? By clicking here you can contact me where you can study your case.
